.fb-comments,.fb-comments span,.fb-comments span iframe[style]{min-width:100%!important;width:100%!important} 
機械学習の面接では、候補者がさまざまな側面から判断されるため、厳格な準備が必要です技術とプログラミングのスキル、ML の概念に関する深い知識など。機械学習の専門家を志望している場合、採用担当者が機械学習の面接でどのような質問をする可能性があるかを知っておくことは非常に重要です。この学習の旅を合理化するために、これらの重要な ML の質問を絞り込みました。これらの質問により、機械学習エンジニア、データ サイエンティスト、計算言語学者、ソフトウェア開発者、ビジネス インテリジェンス (BI) 開発者、自然言語処理 (NLP) 科学者などの仕事に就くことができます。
だから、機械学習で夢のキャリアを築く準備はできていますか?
機械学習の面接でよく聞かれる質問トップ 10 のリストは次のとおりです
機械学習の面接では、厳格な面接プロセスが求められます候補者は、技術的およびプログラミングのスキル、方法の知識、基本的な概念の明確さなど、さまざまな側面で判断されます。機械学習の仕事に応募することを熱望している場合は、採用担当者や採用担当者が一般的に尋ねる機械学習の面接の質問の種類を知ることが重要です。
目次
機械学習新入生向けのインタビューの質問
機械学習の初心者で、この分野での地位を確立したい場合は、ML の専門家の需要が高まっている今がその時です。このセクションの質問は、今後の準備に役立ちます。
ここでは、面接中に直面する可能性のある機械学習面接のよくある質問 (ML 面接の質問) のリストをまとめました。
1.人工知能 (AI)、機械学習 (ML)、ディープ ラーニングという用語について説明してください。
人工知能 (AI) は、インテリジェント マシンを生み出す領域です。 ML とは、経験 (トレーニング データ) とディープ ラーニング (DL) の状態から、大規模なデータ セットの経験から学習するシステムに同化できるシステムを指します。 ML は AI のサブセットと見なすことができます。ディープ ラーニング (DL) は ML ですが、大規模なデータ セットに役立ちます。 The figure below roughly encapsulates the relation between AI, ML, and DL:
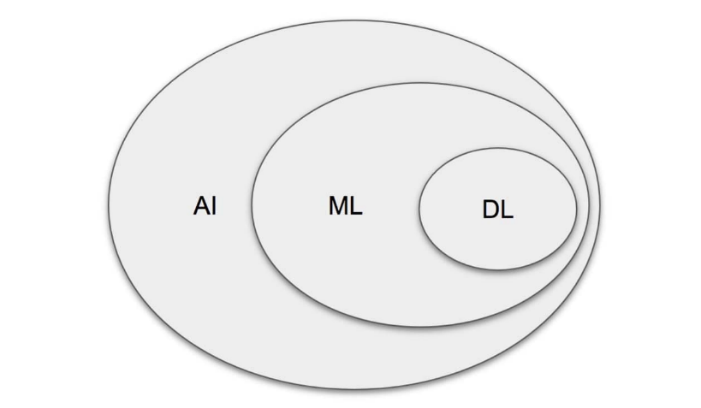
In summary, DL is ML のサブセットであり、両方とも AI のサブセットでした。
追加情報: ASR (自動音声認識) と NLP (自然言語処理) は AI に分類され、ML は多くの場合に利用されるため、ML と DL をオーバーレイします。 NLP および ASR タスク。
TWg93Q4″> ML の学習/トレーニング モデルにはどのような種類がありますか?
ML アルゴリズムは、主にターゲット変数の有無によって分類できます。
A.教師あり学習: [ターゲットが存在する]
機械はラベル付きデータを使用して学習します。モデルは、新しいデータを使用して意思決定を開始する前に、既存のデータ セットでトレーニングされます。
ターゲット変数は連続的です: 線形回帰、多項式回帰、二次回帰です。
ターゲット変数はカテゴリカルです: ロジスティック回帰、 Naive Bayes、KNN、SVM、デシジョン ツリー、勾配ブースティング、ADA ブースティング、バギング、ランダム フォレストなど
B.教師なし学習: [ターゲットが存在しません]
機械は、適切なガイダンスなしで、ラベル付けされていないデータでトレーニングされます。クラスターを作成することにより、データ内のパターンと関係を自動的に推測します。モデルは、データの観察と推定構造を通じて学習します。
主成分分析、因子分析、特異値分解など。
C.強化学習:
モデルは試行錯誤の方法で学習します。この種の学習には、環境と対話してアクションを作成し、そのアクションのエラーまたは報酬を発見するエージェントが関与します。
3.ディープ ラーニングと機械学習の違いは何ですか?
機械学習には、データのパターンから学習して意思決定に適用するアルゴリズムが含まれます。一方、ディープ ラーニングは、データを独自に処理して学習することができ、人間の脳と非常によく似ており、何かを識別して分析し、決定を下します。
主な違いは次のとおりです。
データがシステムに提示される方法。機械学習アルゴリズムは常に構造化データを必要とし、深層学習ネットワークは人工ニューラル ネットワークの層に依存しています。
4.教師あり機械学習と教師なし機械学習の主な違いは何ですか?
5.データセットの作業中に重要な変数をどのように選択しますか?
データセットから重要な変数を選択するには、次のようなさまざまな方法があります:
重要な変数を確定する前に、相関する変数を特定して破棄する 変数は、線形回帰 フォワード、バックワード、およびステップワイズ選択 ラッソ回帰ランダム フォレストおよびプロット変数チャート トップ フィーチャは、使用可能なフィーチャ セットの情報ゲインに基づいて選択できます。
6.これまでに多くの機械学習アルゴリズムが存在します。
使用する機械学習アルゴリズムは、与えられたデータセット内のデータの種類に完全に依存します。データが線形の場合、線形回帰を使用します。データが非線形性を示している場合は、バギング アルゴリズムの方がうまく機能します。ビジネス目的でデータを分析/解釈する場合は、決定木または SVM を使用できます。データセットが画像、動画、音声で構成されている場合、ニューラル ネットワークはソリューションを正確に取得するのに役立ちます。
そのため、特定の状況や特定の状況に使用するアルゴリズムを決定する特定の指標はありません。データセット。 EDA (Exploratory Data Analysis) を使用してデータを調査し、データセットを使用して最適なアルゴリズムを見つける目的を理解する必要があります。 So, it is important to study all the algorithms in detail.
7.共分散と相関は互いにどのように異なるのですか?
1 は正の関係を示し、-1 は負の関係を示し、0 は 2 つの変数が互いに独立していることを示します。
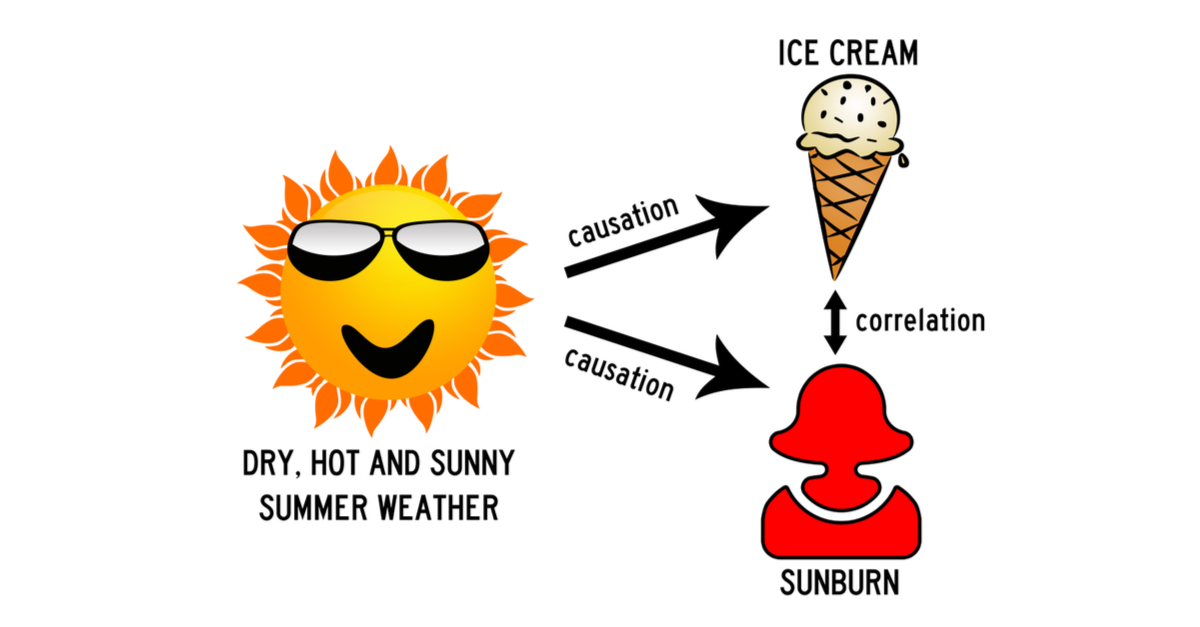
8.因果関係と相関関係の違いを述べてください?
因果関係は、1 つのアクション (X など) が結果 (Y など) を引き起こす状況に適用されますが、相関関係は 1 つのアクション (X) を別のアクションに関連付けるだけです。 (Y) but X does not necessarily cause Y.
9.私たちはほぼ常に機械学習ソフトウェアを見ています。機械学習をハードウェアに適用するにはどうすればよいですか?
機械学習をハードウェアに適用するには、ハードウェア開発言語である System Verilog で ML アルゴリズムを構築し、それを FPGA にプログラムする必要があります。
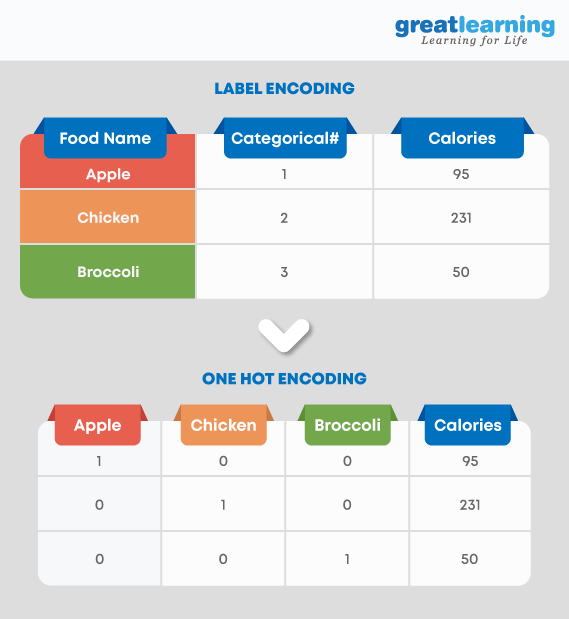
10.ワンホット エンコーディングとラベル エンコーディングについて説明します。
ワンホット エンコーディングは、バイナリ ベクトルとしてのカテゴリ変数の表現です。ラベル エンコーディングは、ラベル/単語を数値形式に変換しています。ワンホット エンコーディングを使用すると、データ セットの次元が増加します。ラベルのエンコードは、データ セットの次元には影響しません。ワンホット エンコーディングでは、変数のレベルごとに新しい変数が作成されますが、ラベル エンコーディングでは、変数のレベルが 1 と 0 としてエンコードされます。
ディープ ラーニング インタビューの質問
ディープ ラーニングは、ニューラル ネットワークで動作する機械学習の一部です。これには、マシンがアクションの背後にある人間のロジックを学習するのに役立つプロセスを設定する、ネットワークの階層構造が含まれます。準備に役立つように、深層学習の面接でよくある質問のリストをまとめました。
11.機械学習で正則化が機能するのはいつですか?
モデルが適合不足または過剰適合し始めると、正則化が必要になります。これは、係数の推定値をゼロに向けて方向転換または正則化する回帰です。柔軟性が低下し、モデルでの学習が妨げられて、オーバーフィッティングのリスクが回避されます。モデルの複雑さが軽減され、予測が向上します。
12.バイアス、分散とは何ですか?また、バイアスと分散のトレードオフとは何を意味しますか?
どちらも機械学習アルゴリズムのエラーです。データセットから正しい観測値を推測するアルゴリズムの柔軟性が限られている場合、バイアスが生じます。一方、分散は、モデルが小さな変動に非常に敏感な場合に発生します。
モデルの構築中に機能を追加すると、複雑さが増し、バイアスは失われますが、分散がいくらか得られます。最適な誤差量を維持するために、ビジネスのニーズに基づいて偏りと分散の間のトレードオフを実行します。
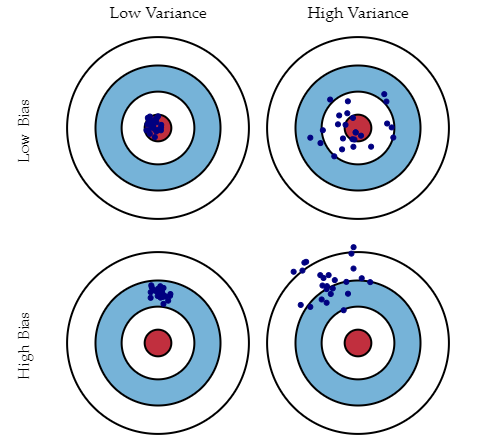 ソース: バイアスと分散のトレードオフを理解する: Scott Fortmann – Roe
ソース: バイアスと分散のトレードオフを理解する: Scott Fortmann – Roe
バイアスは、学習アルゴリズムにおける誤った仮定または過度に単純化された仮定によるエラーを表します。この仮定により、モデルがデータに適合しなくなり、高い予測精度を得たり、トレーニング セットからテスト セットに知識を一般化することが困難になる可能性があります。
分散もエラーです。学習アルゴリズムが複雑すぎる。これが、アルゴリズムがトレーニング データの高度な変動に対して非常に敏感である理由であり、モデルがデータをオーバーフィットする可能性があります。モデルのトレーニング データからあまりにも多くのノイズを運ぶと、テスト データに非常に役立ちます。
バイアス分散分解は、基本的に、バイアス、分散、ビットを追加することで、任意のアルゴリズムからの学習エラーを分解します。基礎となるデータセットのノイズによる削減不可能なエラーの。基本的に、モデルをより複雑にして変数を追加すると、バイアスは失われますが、多少の分散が得られます。誤差を最適に減らすには、バイアスと分散をトレードオフする必要があります。
13. モデルに大きな偏りや大きな分散は必要ありません。標準偏差と分散をどのように関連付けることができますか?
標準偏差とは、平均からのデータの広がりを指します。分散は、各ポイントが平均、つまりすべてのデータポイントの平均と異なる平均程度です。分散の平方根であるため、標準偏差と分散を関連付けることができます。
14.与えられたデータ セットには、平均から 1 標準偏差に沿って広がる欠損値があります。
データが平均に分散している、つまりデータが平均に分散しているとします。したがって、正規分布であると推測できます。正規分布では、データの約 68% が、平均、最頻値、中央値などの平均から 1 標準偏差内にあります。これは、データの約 32% が欠損値の影響を受けないことを意味します。
15.
分散が大きいということは、データの広がりが大きく、対象物にさまざまなデータがあることを直接的に意味します。
16. 通常、フィーチャの分散が大きいと、あまり品質が良くないと見なされます。データセットの分散が大きい場合、どのように処理しますか?
分散が大きいデータセットの場合、バギング アルゴリズムを使用して処理できます。バギング アルゴリズムは、ランダム データから複製されたサンプリングを使用して、データをサブグループに分割します。データが分割された後、ランダム データを使用して、トレーニング アルゴリズムを使用してルールを作成します。次に、ポーリング手法を使用して、モデルのすべての予測結果を結合します。
17.公益事業の不正検出に関するデータ セットが提供されます。分類子モデルを構築し、98.5% のパフォーマンス スコアを達成しました。これは良いモデルですか?はいの場合は、正当化します。
公益事業の不正検出に関するデータセットのバランスが十分ではありません。つまり、バランスが取れていません。このようなデータセットでは、精度スコアは多数派クラスのラベルを正しく予測することしかできないため、パフォーマンスの尺度にはなりませんが、この場合、関心のあるポイントは少数派ラベルを予測することです。しかし、マイノリティはノイズとして扱われ、無視されることがよくあります。そのため、多数派ラベルと比較して少数派ラベルの誤分類の可能性が高くなります。不均衡なデータ セットの場合にモデルのパフォーマンスを評価するには、感度 (真陽性率) または特異度 (真陰性率) を使用して、分類モデルのクラス ラベルごとのパフォーマンスを決定する必要があります。マイノリティ クラス ラベルのパフォーマンスがあまり良くない場合は、次のことを行うことができます。
アンダー サンプリングまたはオーバー サンプリングを使用して、データのバランスを取ることができます。予測しきい値を変更できます。少数派クラスのラベルの重みが大きくなるように、ラベルに重みを割り当てることができます。異常を検出できました。
18.
欠損値または破損した値を処理する簡単な方法は、対応する行または列を削除することです。削除する行または列が多すぎる場合は、欠損値または破損した値を新しい値に置き換えることを検討します。
欠損値を特定して行または列を削除するには、IsNull() および dropna を使用します。 ( ) は Pandas で機能します。また、Pandas の Fillna() 関数は、正しくない値をプレースホルダー値に置き換えます。
19.時系列とは
時系列とは、一連の数値データ ポイントを連続した順序で表したものです。選択したデータ ポイントの移動を指定された期間にわたって追跡し、一定の間隔でデータ ポイントを記録します。時系列では、最小時間または最大時間の入力は必要ありません。アナリストは、時系列を使用して、特定の要件に従ってデータを調べることがよくあります。
<強い>20。 Box-Cox 変換とは?
Box-Cox 変換は、非正規従属変数を正規変数に変換するベキ変換です。これは、正規性が多くの統計手法を使用する際に行われる最も一般的な仮定であるためです。.これにはラムダ パラメータがあり、0 に設定すると、この変換が log-transform と同等であることを意味します。分散の安定化と分布の正規化に使用されます。
21.確率的勾配降下法 (SGD) と勾配降下法 (GD) の違いは何ですか?
勾配降下法と確率的勾配降下法は、損失関数を最小化する一連のパラメーターを見つけるアルゴリズムです。
違いは、Gradient Descend では、すべてのトレーニング サンプルがパラメーターのセットごとに評価されることです。確率的勾配降下法では、識別された一連のパラメーターに対して 1 つのトレーニング サンプルのみが評価されます。
22.バック プロパゲーション テクニックを使用する際の爆発的勾配問題とは何ですか?
大きな誤差勾配が蓄積され、トレーニング中にニューラル ネットワークの重みが大きく変化する場合、それは爆発的勾配問題と呼ばれます。重みの値が大きくなりすぎてオーバーフローし、NaN 値になる場合があります。これにより、モデルが不安定になり、勾配消失問題と同様にモデルの学習が停止します。 This is one of the most commonly asked interview questions on machine learning.
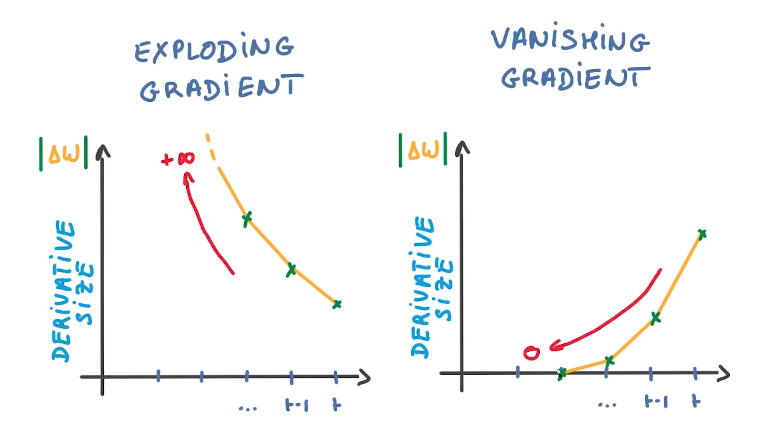
23.デシジョン ツリーの長所と短所をいくつか挙げていただけますか?
デシジョン ツリーの利点は、解釈が容易であること、ノンパラメトリックであるため外れ値に対してロバストであること、調整するパラメーターが比較的少ないことです。
一方で欠点は、オーバーフィットしやすいことです。
24.ランダム フォレストと勾配ブースティング マシンの違いを説明してください。
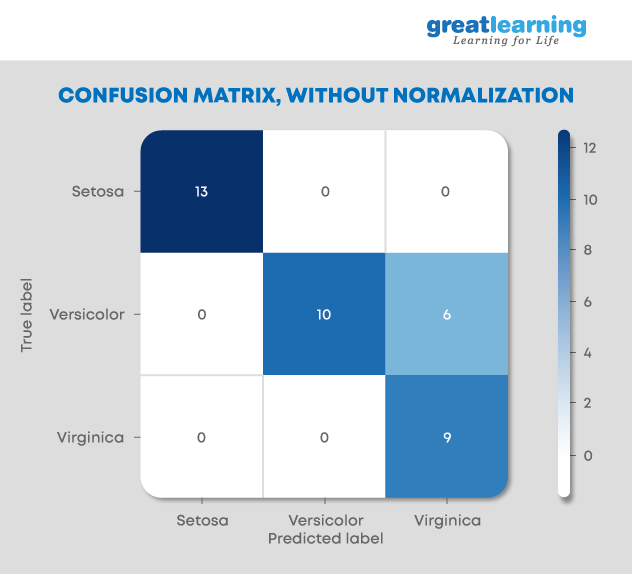
25.混同行列とは何ですか?なぜそれが必要なのですか?
混同行列 (誤差行列とも呼ばれます) は、分類モデルのパフォーマンスを示すために頻繁に使用されるテーブルです。真の値がよく知られている一連のテスト データ。
これにより、アルゴリズム/モデルのパフォーマンスを視覚化できます。これにより、異なるクラス間の混乱を簡単に特定できます。モデル/アルゴリズムのパフォーマンス指標として使用されます。
混同行列は、分類モデルの予測の要約として知られています。正しい予測と間違った予測の数は、カウント値で要約され、各クラス ラベルで分類されました。これにより、分類器によって発生したエラーと、分類器によって発生したエラーの種類に関する情報が得られます。
26.フーリエ変換とは?
フーリエ変換は、時間の関数を周波数の関数に変換する数学的手法です。フーリエ変換は、フーリエ級数と密接に関連しています。任意の時間ベースのパターンを入力として受け取り、可能なすべてのサイクルの全体的なサイクル オフセット、回転速度、および強度を計算します。フーリエ変換は、時間と空間の関数を持っているため、波形に最もよく適用されます。フーリエ変換が波形に適用されると、正弦波に分解されます。
27.連想規則マイニング (ARM) とはどういう意味ですか?
連想規則マイニングは、一緒に発生する特徴 (ディメンション) や、一緒に発生する特徴 (ディメンション) などのデータのパターンを発見する手法の 1 つです。相関しています。主に市場ベースの分析で使用され、アイテムセットがトランザクションでどのくらいの頻度で発生するかを調べます。アソシエーション ルールは、最小サポートと最小信頼度を同時に満たす必要があります。アソシエーション ルールの生成は通常、次の 2 つの異なるステップで構成されます。 「アソシエーション ルールを形成するために、これらの頻繁な項目セットに最小信頼度制約が与えられます。」
支持度は「項目セット」がデータセットに出現する頻度の尺度であり、信頼度は特定のルールが真であることが判明した頻度の尺度です。
28.周縁化とは?プロセスを説明してください。
周辺化とは、確率変数 X の確率を、X と他の変数との同時確率分布が与えられた場合に合計することです。全確率の法則の応用です。
P(X=x)=∑YP(X=x,Y)
同時確率 P(X=x,Y) が与えられると、周辺化を使用して P を見つけることができます(X=x)。
29. 「次元の呪い」というフレーズについて説明してください。
次元の呪いとは、データに特徴が多すぎる状況を指します。
このフレーズは、入力が多すぎる関数を最適化するためにブルート フォースまたはグリッド検索を使用することの難しさ。
次のような他のいくつかの問題を参照することもできます。
観測よりも多くの機能がある場合、リスクがあります。モデルの過剰適合の。特徴が多すぎると、観測をクラスター化するのが難しくなります。ディメンションが多すぎると、データセット内のすべての観測が他のすべての観測から等距離に表示され、意味のあるクラスターを形成できなくなります。
そのような場合、PCA のような次元削減技術が役に立ちます。
30.主成分分析とは?
ここでの考え方は、相互に相関する変数の数を減らすことによって、データ セットの次元を減らすことです。ただし、変動は最大限保持する必要があります。
変数は、主成分として知られる新しい変数セットに変換されます。これらの PC は共分散行列の固有ベクトルであるため、直交しています。
31.主成分分析 (PCA) でコンポーネントのローテーションが重要なのはなぜですか?
PCA のローテーションは、すべてのコンポーネントによって得られる分散内での分離を最大化するため、非常に重要です。コンポーネントがより簡単になります。コンポーネントが回転されていない場合、コンポーネントの分散を記述するために拡張コンポーネントが必要です。
32.外れ値とは外れ値に対処するための 3 つの方法を挙げてください。

データ ポイント他の同様のデータポイントからかなり離れているものは、外れ値として知られています。それらは、実験誤差または測定のばらつきが原因で発生する可能性があります。それらは問題があり、トレーニング プロセスを誤解させる可能性があり、最終的にはトレーニング時間が長くなり、モデルが不正確になり、結果が悪くなる可能性があります。
外れ値に対処する 3 つの方法は次のとおりです。
単変量法 – 1 つの変数で極端な値を持つデータ ポイントを探します
多変量法 – すべての変数で異常な組み合わせを探します
ミンコフスキー エラー – 減少しますトレーニング プロセスにおける潜在的な外れ値の寄与
また読む-機械学習でキャリアを追求する利点
33.正則化と正規化の違いは何ですか?
34.正規化と標準化の違いを説明してください。
正規化と標準化は、特徴のスケーリングに使用される 2 つの非常に一般的な方法です。
35。最も一般的な分布曲線を、アルゴリズムで使用するシナリオとともにリストします。
最も一般的な分布曲線は、ベルヌーイ分布、一様分布、二項分布、正規分布、ポアソン分布、および指数分布。
これらの分布曲線はそれぞれ、さまざまなシナリオで使用されます。
ベルヌーイ分布は、チームが優勝するかどうか、生まれたばかりの子供が男性か女性か、
一様分布は、確率が一定の確率分布です。 1 つのサイコロを振ることは、結果の数が決まっているため、その一例です。
二項分布は、可能な結果が 2 つしかない確率です。接頭辞の「bi」は、2 つまたは 2 つを意味します。.この例は、コイントスです。結果は表か裏のどちらかになります。
正規分布は、変数の値がどのように分布しているかを表します。これは通常、ほとんどの観測値が中央のピークの周りに集まっている対称的な分布です。平均値から離れた値は、両方向で等しく先細りになります。たとえば、教室の生徒の身長です。
ポアソン分布は、特定のイベントが発生する頻度がわかっている場合に、そのイベントが発生する確率を予測するのに役立ちます。ビジネスマンは、特定の日の顧客数を予測し、需要に応じて供給を調整するために使用できます。
指数分布は、特定のイベントが発生するまでの時間。たとえば、車のバッテリーが何ヶ月も持つか。
36.データセットまたは特徴の正規性を確認するにはどうすればよいですか?
視覚的には、プロットを使用して確認できます。正規性チェックのリストは次のとおりです。
Shapiro-Wilk W 検定 Anderson-Darling 検定 Martinez-Iglewicz 検定 Kolmogorov-Smirnov 検定 D’Agostino Skewness 検定
37.線形回帰とは
線形関数は、Y=Mx +C として 2D 平面上の数学関数として定義できます。Y は従属変数、X は独立変数、C です。は切片であり、M は勾配であり、Y は X の関数または Y=F(x) として表すことができます。
X の任意の値で、次を使用して Y の値を計算できます。直線の方程式。多項式の次数を 1 とした Y と X のこの関係は、線形回帰と呼ばれます。
予測モデリングでは、LR は Y=Bo + B1x1 + B2x2 として表されます。
B1 の値とB2 は、特徴と従属変数の間の相関の強さを決定します。
例: $ の株価=切片 + (+/-B1)*(株価の始値) + (+/-B2) *(前日の株式の最高値)
38.回帰と分類を区別します。
回帰と分類は、教師あり機械学習の同じ傘の下に分類されます。それらの主な違いは、回帰の出力変数が数値 (または連続) であるのに対し、分類の出力変数はカテゴリ (または離散) であることです。
例: ある場所の明確な気温を予測することは回帰問題ですが、その日が晴れるか曇るか、雨が降るかを予測することは分類の問題です。
39.ターゲットの不均衡とは何ですか?どうすれば修正できますか?データに対してターゲットの不均衡を実行したシナリオ。このデータを入力するのに適している指標とアルゴリズムはどれですか。
If you have categorical variables as the target when you cluster them together or perform a frequency count on them if there are certain categories which are more in number as compared to others by a very significant number. This is known as the target imbalance.
Example: Target column – 0,0,0,1,0,2,0,0,1,1 [0s: 60%, 1: 30%, 2:10%] 0 are in majority. To fix this, we can perform up-sampling or down-sampling. Before fixing this problem let’s assume that the performance metrics used was confusion metrics. After fixing this problem we can shift the metric system to AUC: ROC. Since we added/deleted data [up sampling or downsampling], we can go ahead with a stricter algorithm like SVM, Gradient boosting or ADA boosting.
40. List all assumptions for data to be met before starting with linear regression.
Before starting linear regression, the assumptions to be met are as follow:
Linear relationship Multivariate normality No or little multicollinearity No auto-correlation Homoscedasticity
41. When does the linear regression line stop rotating or finds an optimal spot where it is fitted on data?
A place where the highest RSquared value is found, is the place where the line comes to rest. RSquared represents the amount of variance captured by the virtual linear regression line with respect to the total variance captured by the dataset.
42. Why is logistic regression a type of classification technique and not a regression? Name the function it is derived from?
Since the target column is categorical, it uses linear regression to create an odd function that is wrapped with a log function to use regression as a classifier. Hence, it is a type of classification technique and not a regression. It is derived from cost function.
43. What could be the issue when the beta value for a certain variable varies way too much in each subset when regression is run on different subsets of the given dataset?
Variations in the beta values in every subset implies that the dataset is heterogeneous. To overcome this problem, we can use a different model for each of the clustered subsets of the dataset or use a non-parametric model such as decision trees.
44. What does the term Variance Inflation Factor mean?
Variation Inflation Factor (VIF) is the ratio of the variance of the model to the variance of the model with only one independent variable. VIF gives the estimate of the volume of multicollinearity in a set of many regression variables.
VIF=Variance of model with one independent variable
45. Which machine learning algorithm is known as the lazy learner and why is it called so?
KNN is a Machine Learning algorithm known as a lazy learner. K-NN is a lazy learner because it doesn’t learn any machine learnt values or variables from the training data but dynamically calculates distance every time it wants to classify, hence memorising the training dataset instead.
Machine Learning Interview Questions for Experienced
We know what the companies are looking for, and with that in mind, we have prepared the set of Machine Learning interview questions an experienced professional may be asked. So, prepare accordingly if you wish to ace the interview in one go.
46. Is it possible to use KNN for image processing?
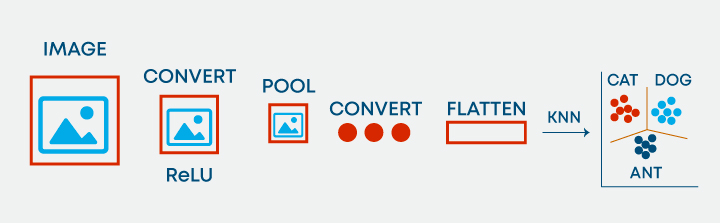
Yes, it is possible to use KNN for image processing. It can be done by converting the 3-dimensional image into a single-dimensional vector and using the same as input to KNN.
47. Differentiate between K-Means and KNN algorithms?
NLP Interview Questions
NLP or Natural Language Processing helps machines analyse natural languages with the intention of learning them. It extracts information from data by applying machine learning algorithms. Apart from learning the basics of NLP, it is important to prepare specifically for the interviews. Check out the top NLP Interview Questions
48. How does the SVM algorithm deal with self-learning?
SVM has a learning rate and expansion rate which takes care of this. The learning rate compensates or penalises the hyperplanes for making all the wrong moves and expansion rate deals with finding the maximum separation area between classes.
49. What are Kernels in SVM? List popular kernels used in SVM along with a scenario of their applications.
The function of the kernel is to take data as input and transform it into the required form. A few popular Kernels used in SVM are as follows: RBF, Linear, Sigmoid, Polynomial, Hyperbolic, Laplace, etc.
50. What is Kernel Trick in an SVM Algorithm?
Kernel Trick is a mathematical function which when applied on data points, can find the region of classification between two different classes. Based on the choice of function, be it linear or radial, which purely depends upon the distribution of data, one can build a classifier.
51. What are ensemble models? Explain how ensemble techniques yield better learning as compared to traditional classification ML algorithms.
An ensemble is a group of models that are used together for prediction both in classification and regression classes. Ensemble learning helps improve ML results because it combines several models. By doing so, it allows for a better predictive performance compared to a single model.
They are superior to individual models as they reduce variance, average out biases, and have lesser chances of overfitting.
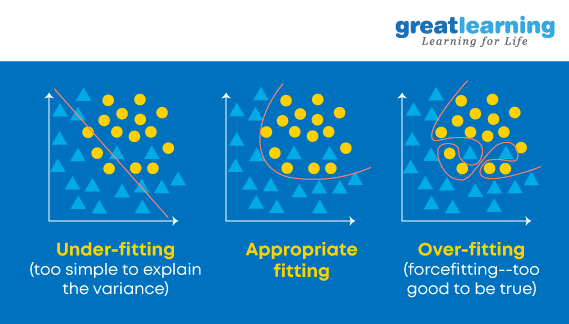
52. What are overfitting and underfitting? Why does the decision tree algorithm suffer often with overfitting problems?
Overfitting is a statistical model or machine learning algorithm which captures the noise of the data. Underfitting is a model or machine learning algorithm which does not fit the data well enough and occurs if the model or algorithm shows low variance but high bias.
In decision trees, overfitting occurs when the tree is designed to perfectly fit all samples in the training data set. This results in branches with strict rules or sparse data and affects the accuracy when predicting samples that aren’t part of the training set.
Also Read: Overfitting and Underfitting in Machine Learning
53. What is OOB error and how does it occur?
For each bootstrap sample, there is one-third of data that was not used in the creation of the tree, i.e., it was out of the sample. This data is referred to as out of bag data. In order to get an unbiased measure of the accuracy of the model over test data, out of bag error is used. The out of bag data is passed for each tree is passed through that tree and the outputs are aggregated to give out of bag error. This percentage error is quite effective in estimating the error in the testing set and does not require further cross-validation.
54. Why boosting is a more stable algorithm as compared to other ensemble algorithms?
Boosting focuses on errors found in previous iterations until they become obsolete. Whereas in bagging there is no corrective loop. This is why boosting is a more stable algorithm compared to other ensemble algorithms.
55. How do you handle outliers in the data?
Outlier is an observation in the data set that is far away from other observations in the data set. We can discover outliers using tools and functions like box plot, scatter plot, Z-Score, IQR score etc. and then handle them based on the visualization we have got. To handle outliers, we can cap at some threshold, use transformations to reduce skewness of the data and remove outliers if they are anomalies or errors.
56. List popular cross validation techniques.
There are mainly six types of cross validation techniques. They are as follow:
K fold Stratified k fold Leave one out Bootstrapping Random search cv Grid search cv
57. Is it possible to test for the probability of improving model accuracy without cross-validation techniques? If yes, please explain.
Yes, it is possible to test for the probability of improving model accuracy without cross-validation techniques. We can do so by running the ML model for say n number of iterations, recording the accuracy. Plot all the accuracies and remove the 5% of low probability values. Measure the left [low] cut off and right [high] cut off. With the remaining 95% confidence, we can say that the model can go as low or as high [as mentioned within cut off points].
58. Name a popular dimensionality reduction algorithm.
Popular dimensionality reduction algorithms are Principal Component Analysis and Factor Analysis.
Principal Component Analysis creates one or more index variables from a larger set of measured variables. Factor Analysis is a model of the measurement of a latent variable. This latent variable cannot be measured with a single variable and is seen through a relationship it causes in a set of y variables.
59. How can we use a dataset without the target variable into supervised learning algorithms?
Input the data set into a clustering algorithm, generate optimal clusters, label the cluster numbers as the new target variable. Now, the dataset has independent and target variables present. This ensures that the dataset is ready to be used in supervised learning algorithms.
60. List all types of popular recommendation systems? Name and explain two personalized recommendation systems along with their ease of implementation.
Popularity based recommendation, content-based recommendation, user-based collaborative filter, and item-based recommendation are the popular types of recommendation systems.
Personalised Recommendation systems are-Content-based recommendation, user-based collaborative filter, and item-based recommendation. User-based collaborative filter and item-based recommendations are more personalised. Ease to maintain: Similarity matrix can be maintained easily with Item-based recommendation.
61. How do we deal with sparsity issues in recommendation systems? How do we measure its effectiveness?説明。
Singular value decomposition can be used to generate the prediction matrix. RMSE is the measure that helps us understand how close the prediction matrix is to the original matrix.
62. Name and define techniques used to find similarities in the recommendation system.
Pearson correlation and Cosine correlation are techniques used to find similarities in recommendation systems.
63. State the limitations of Fixed Basis Function.
Linear separability in feature space doesn’t imply linear separability in input space. So, Inputs are non-linearly transformed using vectors of basic functions with increased dimensionality. Limitations of Fixed basis functions are:
Non-Linear transformations cannot remove overlap between two classes but they can increase overlap. Often it is not clear which basis functions are the best fit for a given task. So, learning the basic functions can be useful over using fixed basis functions. If we want to use only fixed ones, we can use a lot of them and let the model figure out the best fit but that would lead to overfitting the model thereby making it unstable.
64. Define and explain the concept of Inductive Bias with some examples.
Inductive Bias is a set of assumptions that humans use to predict outputs given inputs that the learning algorithm has not encountered yet. When we are trying to learn Y from X and the hypothesis space for Y is infinite, we need to reduce the scope by our beliefs/assumptions about the hypothesis space which is also called inductive bias. Through these assumptions, we constrain our hypothesis space and also get the capability to incrementally test and improve on the data using hyper-parameters. Examples:
We assume that Y varies linearly with X while applying Linear regression. We assume that there exists a hyperplane separating negative and positive examples.
65. Explain the term instance-based learning.
Instance Based Learning is a set of procedures for regression and classification which produce a class label prediction based on resemblance to its nearest neighbors in the training data set. These algorithms just collects all the data and get an answer when required or queried. In simple words they are a set of procedures for solving new problems based on the solutions of already solved problems in the past which are similar to the current problem.
66. Keeping train and test split criteria in mind, is it good to perform scaling before the split or after the split?
Scaling should be done post-train and test split ideally. If the data is closely packed, then scaling post or pre-split should not make much difference.
67. Define precision, recall and F1 Score?
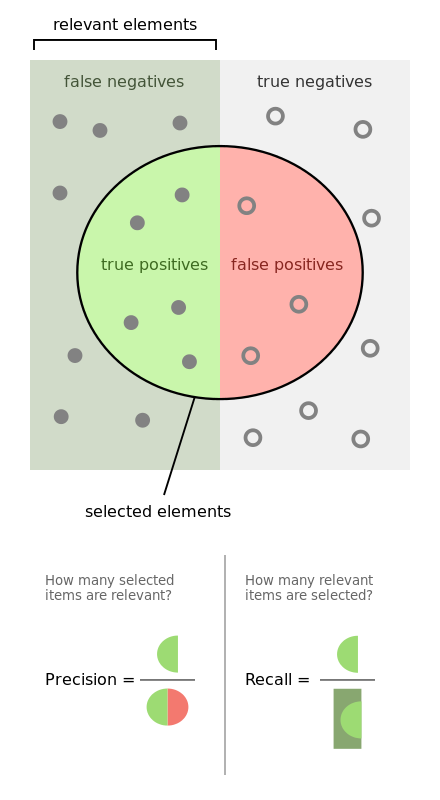
The metric used to access the performance of the classification model is Confusion Metric. Confusion Metric can be further interpreted with the following terms:-
True Positives (TP) – These are the correctly predicted positive values. It implies that the value of the actual class is yes and the value of the predicted class is also yes.
True Negatives (TN) – These are the correctly predicted negative values. It implies that the value of the actual class is no and the value of the predicted class is also no.
False positives and false negatives, these values occur when your actual class contradicts with the predicted class.
Now,
Recall, also known as Sensitivity is the ratio of true positive rate (TP), to all observations in actual class – yes
Recall=TP/(TP+FN)
Precision is the ratio of positive predictive value, which measures the amount of accurate positives model predicted viz a viz number of positives it claims.
Precision=TP/(TP+FP)
Accuracy is the most intuitive performance measure and it is simply a ratio of correctly predicted observation to the total observations.
Accuracy=(TP+TN)/(TP+FP+FN+TN)
F1 Score is the weighted average of Precision and Recall. Therefore, this score takes both false positives and false negatives into account. Intuitively it is not as easy to understand as accuracy, but F1 is usually more useful than accuracy, especially if you have an uneven class distribution. Accuracy works best if false positives and false negatives have a similar cost. If the cost of false positives and false negatives are very different, it’s better to look at both Precision and Recall.
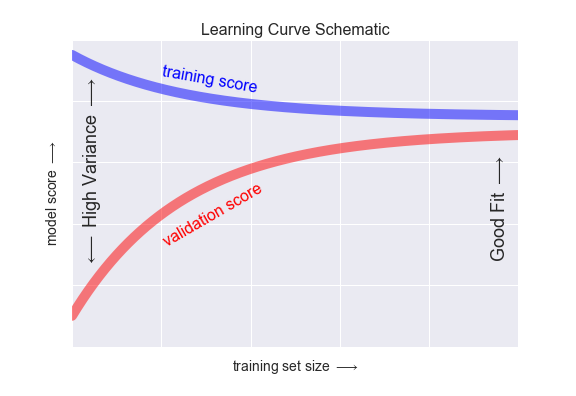
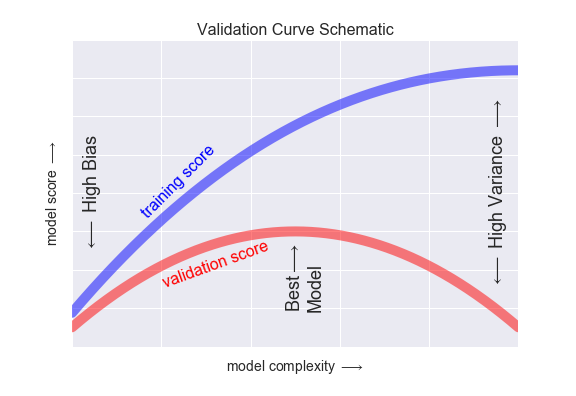
68. Plot validation score and training score with data set size on the x-axis and another plot with model complexity on the x-axis.
For high bias in the models, the performance of the model on the validation data set is similar to the performance on the training data set. For high variance in the models, the performance of the model on the validation set is worse than the performance on the training set.
69. What is Bayes’ Theorem? State at least 1 use case with respect to the machine learning context?
Bayes’ Theorem describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if cancer is related to age, then, using Bayes’ theorem, a person’s age can be used to more accurately assess the probability that they have cancer than can be done without the knowledge of the person’s age.
Chain rule for Bayesian probability can be used to predict the likelihood of the next word in the sentence.
70. What is Naive Bayes? Why is it Naive?
Naive Bayes classifiers are a series of classification algorithms that are based on the Bayes theorem. This family of algorithm shares a common principle which treats every pair of features independently while being classified.
Naive Bayes is considered Naive because the attributes in it (for the class) is independent of others in the same class. This lack of dependence between two attributes of the same class creates the quality of naiveness.
Read more about Naive Bayes.
71. Explain how a Naive Bayes Classifier works.
Naive Bayes classifiers are a family of algorithms which are derived from the Bayes theorem of probability. It works on the fundamental assumption that every set of two features that is being classified is independent of each other and every feature makes an equal and independent contribution to the outcome.
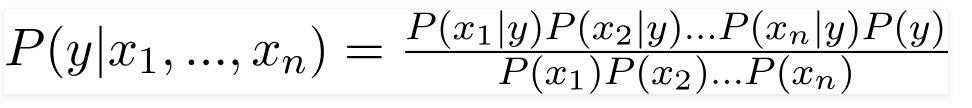
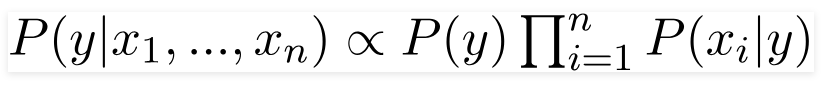
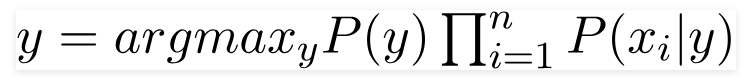
72. What do the terms prior probability and marginal likelihood in context of Naive Bayes theorem mean?
Prior probability is the percentage of dependent binary variables in the data set. If you are given a dataset and dependent variable is either 1 or 0 and percentage of 1 is 65% and percentage of 0 is 35%. Then, the probability that any new input for that variable of being 1 would be 65%.
Marginal likelihood is the denominator of the Bayes equation and it makes sure that the posterior probability is valid by making its area 1.
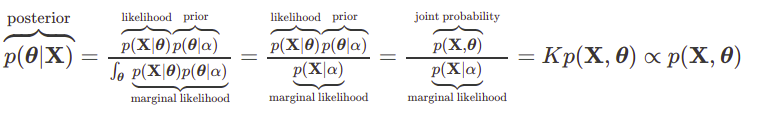
73. Explain the difference between Lasso and Ridge?
Lasso(L1) and Ridge(L2) are the regularization techniques where we penalize the coefficients to find the optimum solution. In ridge, the penalty function is defined by the sum of the squares of the coefficients and for the Lasso, we penalize the sum of the absolute values of the coefficients. Another type of regularization method is ElasticNet, it is a hybrid penalizing function of both lasso and ridge.
74. What’s the difference between probability and likelihood?
Probability is the measure of the likelihood that an event will occur that is, what is the certainty that a specific event will occur? Where-as a likelihood function is a function of parameters within the parameter space that describes the probability of obtaining the observed data.
So the fundamental difference is, Probability attaches to possible results; likelihood attaches to hypotheses.
75. Why would you Prune your tree?
In the context of data science or AIML, pruning refers to the process of reducing redundant branches of a decision tree. Decision Trees are prone to overfitting, pruning the tree helps to reduce the size and minimizes the chances of overfitting. Pruning involves turning branches of a decision tree into leaf nodes and removing the leaf nodes from the original branch. It serves as a tool to perform the tradeoff.
76. Model accuracy or Model performance? Which one will you prefer and why?
This is a trick question, one should first get a clear idea, what is Model Performance? If Performance means speed, then it depends upon the nature of the application, any application related to the real-time scenario will need high speed as an important feature. Example: The best of Search Results will lose its virtue if the Query results do not appear fast.
If Performance is hinted at Why Accuracy is not the most important virtue – For any imbalanced data set, more than Accuracy, it will be an F1 score than will explain the business case and in case data is imbalanced, then Precision and Recall will be more important than rest.
77. List the advantages and limitations of the Temporal Difference Learning Method.
Temporal Difference Learning Method is a mix of Monte Carlo method and Dynamic programming method. Some of the advantages of this method include:
It can learn in every step online or offline. It can learn from a sequence which is not complete as well. It can work in continuous environments. It has lower variance compared to MC method and is more efficient than MC method.
Limitations of TD method are:
It is a biased estimation. It is more sensitive to initialization.
78. How would you handle an imbalanced dataset?
Sampling Techniques can help with an imbalanced dataset. There are two ways to perform sampling, Under Sample or Over Sampling.
In Under Sampling, we reduce the size of the majority class to match minority class thus help by improving performance w.r.t storage and run-time execution, but it potentially discards useful information.
For Over Sampling, we upsample the Minority class and thus solve the problem of information loss, however, we get into the trouble of having Overfitting.
There are other techniques as well –
Cluster-Based Over Sampling – In this case, the K-means clustering algorithm is independently applied to minority and majority class instances. This is to identify clusters in the dataset. Subsequently, each cluster is oversampled such that all clusters of the same class have an equal number of instances and all classes have the same size
Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) – A subset of data is taken from the minority class as an example and then new synthetic similar instances are created which are then added to the original dataset. This technique is good for Numerical data points.
79. Mention some of the EDA Techniques?
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) helps analysts to understand the data better and forms the foundation of better models.
Visualization
Univariate visualization Bivariate visualization Multivariate visualization
Missing Value Treatment – Replace missing values with Either Mean/Median
Outlier Detection – Use Boxplot to identify the distribution of Outliers, then Apply IQR to set the boundary for IQR
Transformation – Based on the distribution, apply a transformation on the features
Scaling the Dataset – Apply MinMax, Standard Scaler or Z Score Scaling mechanism to scale the data.
Feature Engineering – Need of the domain, and SME knowledge helps Analyst find derivative fields which can fetch more information about the nature of the data
Dimensionality reduction — Helps in reducing the volume of data without losing much information
80. Mention why feature engineering is important in model building and list out some of the techniques used for feature engineering.
Algorithms necessitate features with some specific characteristics to work appropriately. The data is initially in a raw form. You need to extract features from this data before supplying it to the algorithm. This process is called feature engineering. When you have relevant features, the complexity of the algorithms reduces. Then, even if a non-ideal algorithm is used, results come out to be accurate.
Feature engineering primarily has two goals:
Prepare the suitable input data set to be compatible with the machine learning algorithm constraints. Enhance the performance of machine learning models.
Some of the techniques used for feature engineering include Imputation, Binning, Outliers Handling, Log transform, grouping operations, One-Hot encoding, Feature split, Scaling, Extracting date.
81. Differentiate between Statistical Modeling and Machine Learning?
Machine learning models are about making accurate predictions about the situations, like Foot Fall in restaurants, Stock-Price, etc. where-as, Statistical models are designed for inference about the relationships between variables, as What drives the sales in a restaurant, is it food or Ambience.
82. Differentiate between Boosting and Bagging?
Bagging and Boosting are variants of Ensemble Techniques.
Bootstrap Aggregation or bagging is a method that is used to reduce the variance for algorithms having very high variance. Decision trees are a particular family of classifiers which are susceptible to having high bias.
Decision trees have a lot of sensitiveness to the type of data they are trained on. Hence generalization of results is often much more complex to achieve in them despite very high fine-tuning. The results vary greatly if the training data is changed in decision trees.
Hence bagging is utilised where multiple decision trees are made which are trained on samples of the original data and the final result is the average of all these individual models.
Boosting is the process of using an n-weak classifier system for prediction such that every weak classifier compensates for the weaknesses of its classifiers. By weak classifier, we imply a classifier which performs poorly on a given data set.
It’s evident that boosting is not an algorithm rather it’s a process. Weak classifiers used are generally logistic regression, shallow decision trees etc.
There are many algorithms which make use of boosting processes but two of them are mainly used: Adaboost and Gradient Boosting and XGBoost.
83. What is the significance of Gamma and Regularization in SVM?
The gamma defines influence. Low values meaning ‘far’ and high values meaning ‘close’. If gamma is too large, the radius of the area of influence of the support vectors only includes the support vector itself and no amount of regularization with C will be able to prevent overfitting. If gamma is very small, the model is too constrained and cannot capture the complexity of the data.
The regularization parameter (lambda) serves as a degree of importance that is given to miss-classifications. This can be used to draw the tradeoff with OverFitting.
84. Define ROC curve work
The graphical representation of the contrast between true positive rates and the false positive rate at various thresholds is known as the ROC curve. It is used as a proxy for the trade-off between true positives vs the false positives.
85. What is the difference between a generative and discriminative model?
A generative model learns the different categories of data. On the other hand, a discriminative model will only learn the distinctions between different categories of data. Discriminative models perform much better than the generative models when it comes to classification tasks.
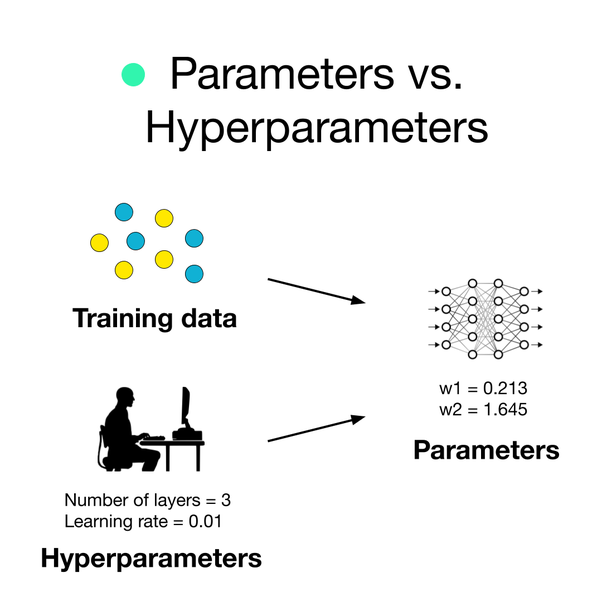
86. What are hyperparameters and how are they different from parameters?
A parameter is a variable that is internal to the model and whose value is estimated from the training data. They are often saved as part of the learned model. Examples include weights, biases etc.
A hyperparameter is a variable that is external to the model whose value cannot be estimated from the data. They are often used to estimate model parameters. The choice of parameters is sensitive to implementation. Examples include learning rate, hidden layers etc.
87. What is shattering a set of points? Explain VC dimension.
In order to shatter a given configuration of points, a classifier must be able to, for all possible assignments of positive and negative for the points, perfectly partition the plane such that positive points are separated from negative points. For a configuration of n points, there are 2n possible assignments of positive or negative.
When choosing a classifier, we need to consider the type of data to be classified and this can be known by VC dimension of a classifier. It is defined as cardinality of the largest set of points that the classification algorithm i.e. the classifier can shatter. In order to have a VC dimension of at least n, a classifier must be able to shatter a single given configuration of n points.
88. What are some differences between a linked list and an array?
Arrays and Linked lists are both used to store linear data of similar types. However, there are a few difference between them.
89. What is the meshgrid () method and the contourf () method? State some usesof both.
The meshgrid( ) function in numpy takes two arguments as input: range of x-values in the grid, range of y-values in the grid whereas meshgrid needs to be built before the contourf( ) function in matplotlib is used which takes in many inputs: x-values, y-values, fitting curve (contour line) to be plotted in grid, colours etc.
Meshgrid () function is used to create a grid using 1-D arrays of x-axis inputs and y-axis inputs to represent the matrix indexing. Contourf () is used to draw filled contours using the given x-axis inputs, y-axis inputs, contour line, colours etc.
90. Describe a hash table.
Hashing is a technique for identifying unique objects from a group of similar objects. Hash functions are large keys converted into small keys in hashing techniques. The values of hash functions are stored in data structures which are known hash table.
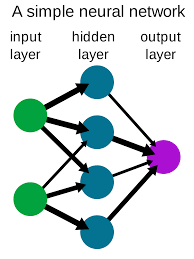
91. List the advantages and disadvantages of using Neural Networks.
Advantages:
We can store information on the entire network instead of storing it in a database. It has the ability to work and give a good accuracy even with inadequate information. A neural network has parallel processing ability and distributed memory.
Disadvantages:
Neural Networks requires processors which are capable of parallel processing. It’s unexplained functioning of the network is also quite an issue as it reduces the trust in the network in some situations like when we have to show the problem we noticed to the network. Duration of the network is mostly unknown. We can only know that the training is finished by looking at the error value but it doesn’t give us optimal results.
92. You have to train a 12GB dataset using a neural network with a machine which has only 3GB RAM. How would you go about it?
We can use NumPy arrays to solve this issue. Load all the data into an array. In NumPy, arrays have a property to map the complete dataset without loading it completely in memory. We can pass the index of the array, dividing data into batches, to get the data required and then pass the data into the neural networks. But be careful about keeping the batch size normal.
Machine Learning Coding Interview Questions
93. Write a simple code to binarize data.
Conversion of data into binary values on the basis of certain threshold is known as binarizing of data. Values below the threshold are set to 0 and those above the threshold are set to 1 which is useful for feature engineering.
Code:
from sklearn.preprocessing import Binarizer import pandas import numpy names_list=[‘Alaska’,’Pratyush’,’Pierce’,’Sandra’,’Soundarya’,’Meredith’,’Richard’,’Jackson’,’Tom’,’Joe’] data_frame=pandas.read_csv(url, names=names_list) array=dataframe.values # Splitting the array into input and output A=array [: 0:7] B=array [:7] binarizer=Binarizer(threshold=0.0). fit(X) binaryA=binarizer.transform(A) numpy.set_printoptions(precision=5) print (binaryA [0:7:])
Machine Learning Using Python Interview Questions
94. What is an Array?
The array is defined as a collection of similar items, stored in a contiguous manner. Arrays is an intuitive concept as the need to group similar objects together arises in our day to day lives. Arrays satisfy the same need. How are they stored in the memory? Arrays consume blocks of data, where each element in the array consumes one unit of memory. The size of the unit depends on the type of data being used. For example, if the data type of elements of the array is int, then 4 bytes of data will be used to store each element. For character data type, 1 byte will be used. This is implementation specific, and the above units may change from computer to computer.
Example:
fruits=[‘apple’, banana’, pineapple’]
In the above case, fruits is a list that comprises of three fruits. To access them individually, we use their indexes. Python and C are 0-indexed languages, that is, the first index is 0. MATLAB on the contrary starts from 1, and thus is a 1-indexed language.
95. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using an Array?
Advantages: Random access is enabled Saves memory Cache friendly Predictable compile timing Helps in re-usability of code Disadvantages: Addition and deletion of records is time consuming even though we get the element of interest immediately through random access. This is due to the fact that the elements need to be reordered after insertion or deletion. If contiguous blocks of memory are not available in the memory, then there is an overhead on the CPU to search for the most optimal contiguous location available for the requirement.
Now that we know what arrays are, we shall understand them in detail by solving some interview questions. Before that, let us see the functions that Python as a language provides for arrays, also known as, lists.
append() – Adds an element at the end of the list
copy() – returns a copy of a list.
reverse() – reverses the elements of the list
sort() – sorts the elements in ascending order by default.
96. What is Lists in Python?
Lists is an effective data structure provided in python. There are various functionalities associated with the same. Let us consider the scenario where we want to copy a list to another list. If the same operation had to be done in C programming language, we would have to write our own function to implement the same.
On the contrary, Python provides us with a function called copy. We can copy a list to another just by calling the copy function.
new_list=old_list.copy()
We need to be careful while using the function. copy() is a shallow copy function, that is, it only stores the references of the original list in the new list. If the given argument is a compound data structure like a list then python creates another object of the same type (in this case, a new list) but for everything inside old list, only their reference is copied. Essentially, the new list consists of references to the elements of the older list.
Hence, upon changing the original list, the new list values also change. This can be dangerous in many applications. Therefore, Python provides us with another functionality called as deepcopy. Intuitively, we may consider that deepcopy() would follow the same paradigm, and the only difference would be that for each element we will recursively call deepcopy. Practically, this is not the case.
deepcopy() preserves the graphical structure of the original compound data. Let us understand this better with the help of an example:
import copy.deepcopy a=[1,2] b=[a,a] # there’s only 1 object a c=deepcopy(b) # check the result by executing these lines c[0] is a # return False, a new object a’is created c[0] is c[1] # return True, c is [a’,a’] not [a’,a”]
This is the tricky part, during the process of deepcopy() a hashtable implemented as a dictionary in python is used to map: old_object reference onto new_object reference.
Therefore, this prevents unnecessary duplicates and thus preserves the structure of the copied compound data structure. Thus, in this case, c[0] is not equal to a, as internally their addresses are different.
Normal copy >>> a=[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] >>> b=list(a) >>> a [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] >>> b [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] >>> a[0][1]=10 >>> a [[1, 10, 3], [4, 5, 6]] >>> b # b changes too-> Not a deepcopy. [[1, 10, 3], [4, 5, 6]] Deep copy >>> import copy >>> b=copy.deepcopy(a) >>> a [[1, 10, 3], [4, 5, 6]] >>> b [[1, 10, 3], [4, 5, 6]] >>> a[0][1]=9 >>> a [[1, 9, 3], [4, 5, 6]] >>> b # b doesn’t change-> Deep Copy [[1, 10, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
Now that we have understood the concept of lists, let us solve interview questions to get better exposure on the same.
97. Given an array of integers where each element represents the max number of steps that can be made forward from that element. The task is to find the minimum number of jumps to reach the end of the array (starting from the first element). If an element is 0, then cannot move through that element.
Solution: This problem is famously called as end of array problem. We want to determine the minimum number of jumps required in order to reach the end. The element in the array represents the maximum number of jumps that, that particular element can take.
Let us understand how to approach the problem initially.
We need to reach the end. Therefore, let us have a count that tells us how near we are to the end. Consider the array A=[1,2,3,1,1]
In the above example we can go from > 2->3-> 1-> 1-4 jumps 1-> 2-> 1-> 1-3 jumps 1-> 2-> 3-> 1-3 jumps
Hence, we have a fair idea of the problem. Let us come up with a logic for the same.
Let us start from the end and move backwards as that makes more sense intuitionally. We will use variables right and prev_r denoting previous right to keep track of the jumps.
Initially, right=prev_r=the last but one element. We consider the distance of an element to the end, and the number of jumps possible by that element. Therefore, if the sum of the number of jumps possible and the distance is greater than the previous element, then we will discard the previous element and use the second element’s value to jump. Try it out using a pen and paper first. The logic will seem very straight forward to implement. Later, implement it on your own and then verify with the result.
def min_jmp(arr): n=len(arr) right=prev_r=n-1 count=0 # We start from rightmost index and travesre array to find the leftmost index # from which we can reach index’right’while True: for j in (range(prev_r-1,-1,-1)): if j + arr[j] >=prev_r: right=j if prev_r !=right: prev_r=right else: break count +=1 return count if right==0 else-1 # Enter the elements separated by a space arr=list(map(int, input().split())) print(min_jmp(n, arr))
98. Given a string S consisting only ‘a’s and ‘b’s, print the last index of the ‘b’ present in it.
When we have are given a string of a’s and b’s, we can immediately find out the first location of a character occurring. Therefore, to find the last occurrence of a character, we reverse the string and find the first occurrence, which is equivalent to the last occurrence in the original string.
Here, we are given input as a string. Therefore, we begin by splitting the characters element wise using the function split. Later, we reverse the array, find the first occurrence position value, and get the index by finding the value len – position-1, where position is the index value.
def split(word): return [(char) for char in word] a=input() a=split(a) a_rev=a[::-1] pos=-1 for i in range(len(a_rev)): if a_rev[i]==‘b’: pos=len(a_rev)-i-1 print(pos) break else: continue if pos==-1: print(-1)
99. Rotate the elements of an array by d positions to the left. Let us initially look at an example.
A=[1,2,3,4,5] A <<2 [3,4,5,1,2] A<<3 [4,5,1,2,3]
There exists a pattern here, that is, the first d elements are being interchanged with last n-d +1 elements. Therefore we can just swap the elements. Correct? What if the size of the array is huge, say 10000 elements. There are chances of memory error, run-time error etc. Therefore, we do it more carefully. We rotate the elements one by one in order to prevent the above errors, in case of large arrays.
# Rotate all the elements left by 1 position def rot_left_once ( arr): n=len( arr) tmp=arr [0] for i in range ( n-1): #[0,n-2] arr[i]=arr[i + 1] arr[n-1]=tmp # Use the above function to repeat the process for d times. def rot_left (arr, d): n=len (arr) for i in range (d): rot_left_once ( arr, n) arr=list( map( int, input().split())) rot=int( input()) leftRotate ( arr, rot) for i in range( len(arr)): print( arr[i], end=”)
100. Water Trapping Problem
Given an array arr[] of N non-negative integers which represents the height of blocks at index I, where the width of each block is 1. Compute how much water can be trapped in between blocks after raining.
# Structure is like below:
# | |
# |_|
# answer is we can trap two units of water.
Solution: We are given an array, where each element denotes the height of the block. One unit of height is equal to one unit of water, given there exists space between the 2 elements to store it. Therefore, we need to find out all such pairs that exist which can store water. We need to take care of the possible cases:
There should be no overlap of water saved Water should not overflow
Therefore, let us find start with the extreme elements, and move towards the centre.
n=int(input()) arr=[int(i) for i in input().split()] left, right=[arr[0]], [0] * n # left=[arr[0]] #right=[ 0 0 0 0…0] n terms right[n-1]=arr[-1] # right most element
# we use two arrays left[ ] and right[ ], which keep track of elements greater than all
# elements the order of traversal respectively.
for elem in arr[1: ]: left.append(max(left[-1], elem) ) for i in range( len( arr)-2,-1,-1): right[i]=max( arr[i] , right[i+1] ) water=0 # once we have the arrays left, and right, we can find the water capacity between these arrays. for i in range( 1, n-1): add_water=min( left[i-1], right[i])-arr[i] if add_water > 0: water +=add_water print(water)
101. Explain Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues.
Ans. Linear transformations are helpful to understand using eigenvectors. They find their prime usage in the creation of covariance and correlation matrices in data science.
Simply put, eigenvectors are directional entities along which linear transformation features like compression, flip etc. can be applied.
Eigenvalues are the magnitude of the linear transformation features along each direction of an Eigenvector.
102. How would you define the number of clusters in a clustering algorithm?
Ans. The number of clusters can be determined by finding the silhouette score. Often we aim to get some inferences from data using clustering techniques so that we can have a broader picture of a number of classes being represented by the data. In this case, the silhouette score helps us determine the number of cluster centres to cluster our data along.
Another technique that can be used is the elbow method.
103. What are the performance metrics that can be used to estimate the efficiency of a linear regression model?
Ans. The performance metric that is used in this case is:
Mean Squared Error R2 score Adjusted R2 score Mean Absolute score
104. What is the default method of splitting in decision trees?
The default method of splitting in decision trees is the Gini Index. Gini Index is the measure of impurity of a particular node.
This can be changed by making changes to classifier parameters.
105. How is p-value useful?
Ans. The p-value gives the probability of the null hypothesis is true. It gives us the statistical significance of our results. In other words, p-value determines the confidence of a model in a particular output.
106. Can logistic regression be used for classes more than 2?
Ans. No, logistic regression cannot be used for classes more than 2 as it is a binary classifier. For multi-class classification algorithms like Decision Trees, Naïve Bayes’ Classifiers are better suited.
107. What are the hyperparameters of a logistic regression model?
Ans. Classifier penalty, classifier solver and classifier C are the trainable hyperparameters of a Logistic Regression Classifier. These can be specified exclusively with values in Grid Search to hyper tune a Logistic Classifier.
108. Name a few hyper-parameters of decision trees?
Ans. The most important features which one can tune in decision trees are:
Splitting criteria Min_leaves Min_samples Max_depth
109. How to deal with multicollinearity?
Ans. Multi collinearity can be dealt with by the following steps:
Remove highly correlated predictors from the model. Use Partial Least Squares Regression (PLS) or Principal Components Analysis
110. What is Heteroscedasticity?
Ans. It is a situation in which the variance of a variable is unequal across the range of values of the predictor variable.
It should be avoided in regression as it introduces unnecessary variance.
111. Is ARIMA model a good fit for every time series problem?
Ans. No, ARIMA model is not suitable for every type of time series problem. There are situations where ARMA model and others also come in handy.
ARIMA is best when different standard temporal structures require to be captured for time series data.
112. How do you deal with the class imbalance in a classification problem?
Ans. Class imbalance can be dealt with in the following ways:
Using class weights Using Sampling Using SMOTE Choosing loss functions like Focal Loss
113. What is the role of cross-validation?
Ans. Cross-validation is a technique which is used to increase the performance of a machine learning algorithm, where the machine is fed sampled data out of the same data for a few times. The sampling is done so that the dataset is broken into small parts of the equal number of rows, and a random part is chosen as the test set, while all other parts are chosen as train sets.
114. What is a voting model?
Ans. A voting model is an ensemble model which combines several classifiers but to produce the final result, in case of a classification-based model, takes into account, the classification of a certain data point of all the models and picks the most vouched/voted/generated option from all the given classes in the target column.
115. How to deal with very few data samples? Is it possible to make a model out of it?
Ans. If very few data samples are there, we can make use of oversampling to produce new data points. In this way, we can have new data points.
116. What are the hyperparameters of an SVM?
Ans. The gamma value, c value and the type of kernel are the hyperparameters of an SVM model.
117. What is Pandas Profiling?
Ans. Pandas profiling is a step to find the effective number of usable data. It gives us the statistics of NULL values and the usable values and thus makes variable selection and data selection for building models in the preprocessing phase very effective.
118. What impact does correlation have on PCA?
Ans. If data is correlated PCA does not work well. Because of the correlation of variables the effective variance of variables decreases. Hence correlated data when used for PCA does not work well.
119. How is PCA different from LDA?
Ans. PCA is unsupervised. LDA is unsupervised.
PCA takes into consideration the variance. LDA takes into account the distribution of classes.
120. What distance metrics can be used in KNN?
Ans. Following distance metrics can be used in KNN.
Manhattan Minkowski Tanimoto Jaccard Mahalanobis
121. Which metrics can be used to measure correlation of categorical data?
Ans. Chi square test can be used for doing so. It gives the measure of correlation between categorical predictors.
122. Which algorithm can be used in value imputation in both categorical and continuous categories of data?
Ans. KNN is the only algorithm that can be used for imputation of both categorical and continuous variables.
123. When should ridge regression be preferred over lasso?
Ans. We should use ridge regression when we want to use all predictors and not remove any as it reduces the coefficient values but does not nullify them.
124. Which algorithms can be used for important variable selection?
Ans. Random Forest, Xgboost and plot variable importance charts can be used for variable selection.
125. What ensemble technique is used by Random forests?
Ans. Bagging is the technique used by Random Forests. Random forests are a collection of trees which work on sampled data from the original dataset with the final prediction being a voted average of all trees.
126. What ensemble technique is used by gradient boosting trees?
Ans. Boosting is the technique used by GBM.
127. If we have a high bias error what does it mean? How to treat it?
Ans. High bias error means that that model we are using is ignoring all the important trends in the model and the model is underfitting.
To reduce underfitting:
We need to increase the complexity of the model Number of features need to be increased
Sometimes it also gives the impression that the data is noisy. Hence noise from data should be removed so that most important signals are found by the model to make effective predictions.
Increasing the number of epochs results in increasing the duration of training of the model. It’s helpful in reducing the error.
128. Which type of sampling is better for a classification model and why?
Ans. Stratified sampling is better in case of classification problems because it takes into account the balance of classes in train and test sets. The proportion of classes is maintained and hence the model performs better. In case of random sampling of data, the data is divided into two parts without taking into consideration the balance classes in the train and test sets. Hence some classes might be present only in tarin sets or validation sets. Hence the results of the resulting model are poor in this case.
129. What is a good metric for measuring the level of multicollinearity?
Ans. VIF or 1/tolerance is a good measure of measuring multicollinearity in models. VIF is the percentage of the variance of a predictor which remains unaffected by other predictors. So higher the VIF value, greater is the multicollinearity amongst the predictors.
A rule of thumb for interpreting the variance inflation factor:
1=not correlated. Between 1 and 5=moderately correlated. Greater than 5=highly correlated.
130. When can be a categorical value treated as a continuous variable and what effect does it have when done so?
Ans. A categorical predictor can be treated as a continuous one when the nature of data points it represents is ordinal. If the predictor variable is having ordinal data then it can be treated as continuous and its inclusion in the model increases the performance of the model.
131. What is the role of maximum likelihood in logistic regression.
Ans. Maximum likelihood equation helps in estimation of most probable values of the estimator’s predictor variable coefficients which produces results which are the most likely or most probable and are quite close to the truth values.
132. Which distance do we measure in the case of KNN?
Ans. The hamming distance is measured in case of KNN for the determination of nearest neighbours. Kmeans uses euclidean distance.
133. What is a pipeline?
Ans. A pipeline is a sophisticated way of writing software such that each intended action while building a model can be serialized and the process calls the individual functions for the individual tasks. The tasks are carried out in sequence for a given sequence of data points and the entire process can be run onto n threads by use of composite estimators in scikit learn.
134. Which sampling technique is most suitable when working with time-series data?
Ans. We can use a custom iterative sampling such that we continuously add samples to the train set. We only should keep in mind that the sample used for validation should be added to the next train sets and a new sample is used for validation.
135. What are the benefits of pruning?
Ans. Pruning helps in the following:
Reduces overfitting Shortens the size of the tree Reduces complexity of the model Increases bias
136. What is normal distribution?
Ans. The distribution having the below properties is called normal distribution.
The mean, mode and median are all equal. The curve is symmetric at the center (i.e. around the mean, μ). Exactly half of the values are to the left of center and exactly half the values are to the right. The total area under the curve is 1.
137. What is the 68 per cent rule in normal distribution?
Ans. The normal distribution is a bell-shaped curve. Most of the data points are around the median. Hence approximately 68 per cent of the data is around the median. Since there is no skewness and its bell-shaped.
138. What is a chi-square test?
Ans. A chi-square determines if a sample data matches a population.
A chi-square test for independence compares two variables in a contingency table to see if they are related.
A very small chi-square test statistics implies observed data fits the expected data extremely well.
139. What is a random variable?
Ans. A Random Variable is a set of possible values from a random experiment. Example: Tossing a coin: we could get Heads or Tails. Rolling of a dice: we get 6 values
140. What is the degree of freedom?
Ans. It is the number of independent values or quantities which can be assigned to a statistical distribution. It is used in Hypothesis testing and chi-square test.
141. Which kind of recommendation system is used by amazon to recommend similar items?
Ans. Amazon uses a collaborative filtering algorithm for the recommendation of similar items. It’s a user to user similarity based mapping of user likeness and susceptibility to buy.
142. What is a false positive?
Ans. It is a test result which wrongly indicates that a particular condition or attribute is present.
Example – “Stress testing, a routine diagnostic tool used in detecting heart disease, results in a significant number of false positives in women”
143. What is a false negative?
Ans. A test result which wrongly indicates that a particular condition or attribute is absent.
Example – “it’s possible to have a false negative—the test says you aren’t pregnant when you are”
144. What is the error term composed of in regression?
Ans. Error is a sum of bias error+variance error+ irreducible error in regression. Bias and variance error can be reduced but not the irreducible error.
145. Which performance metric is better R2 or adjusted R2?
Ans. Adjusted R2 because the performance of predictors impacts it. R2 is independent of predictors and shows performance improvement through increase if the number of predictors is increased.
146. What’s the difference between Type I and Type II error?
Type I and Type II error in machine learning refers to false values. Type I is equivalent to a False positive while Type II is equivalent to a False negative. In Type I error, a hypothesis which ought to be accepted doesn’t get accepted. Similarly, for Type II error, the hypothesis gets rejected which should have been accepted in the first place.
147. What do you understand by L1 and L2 regularization?
L2 regularization: It tries to spread error among all the terms. L2 corresponds to a Gaussian prior.
L1 regularization: It is more binary/sparse, with many variables either being assigned a 1 or 0 in weighting. L1 corresponds to setting a Laplacean prior on the terms.
148. Which one is better, Naive Bayes Algorithm or Decision Trees?
Although it depends on the problem you are solving, but some general advantages are following:
Naive Bayes:
Work well with small dataset compared to DT which need more data Lesser overfitting Smaller in size and faster in processing
Decision Trees:
Decision Trees are very flexible, easy to understand, and easy to debug No preprocessing or transformation of features required Prone to overfitting but you can use pruning or Random forests to avoid that.
149. What do you mean by the ROC curve?
Receiver operating characteristics (ROC curve): ROC curve illustrates the diagnostic ability of a binary classifier. It is calculated/created by plotting True Positive against False Positive at various threshold settings. The performance metric of ROC curve is AUC (area under curve). Higher the area under the curve, better the prediction power of the model.
150. What do you mean by AUC curve?
AUC (area under curve). Higher the area under the curve, better the prediction power of the model.
151. What is log likelihood in logistic regression?
It is the sum of the likelihood residuals. At record level, the natural log of the error (residual) is calculated for each record, multiplied by minus one, and those values are totaled. That total is then used as the basis for deviance (2 x ll) and likelihood (exp(ll)).
The same calculation can be applied to a naive model that assumes absolutely no predictive power, and a saturated model assuming perfect predictions.
The likelihood values are used to compare different models, while the deviances (test, naive, and saturated) can be used to determine the predictive power and accuracy. Logistic regression accuracy of the model will always be 100 percent for the development data set, but that is not the case once a model is applied to another data set.
152. How would you evaluate a logistic regression model?
Model Evaluation is a very important part in any analysis to answer the following questions,
How well does the model fit the data?, Which predictors are most important?, Are the predictions accurate?
So the following are the criterion to access the model performance,
1. Akaike Information Criteria (AIC): In simple terms, AIC estimates the relative amount of information lost by a given model. So the less information lost the higher the quality of the model. Therefore, we always prefer models with minimum AIC.
2. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC curve): ROC curve illustrates the diagnostic ability of a binary classifier. It is calculated/created by plotting True Positive against False Positive at various threshold settings. The performance metric of ROC curve is AUC (area under curve). Higher the area under the curve, better the prediction power of the model.
3. Confusion Matrix: In order to find out how well the model does in predicting the target variable, we use a confusion matrix/classification rate. It is nothing but a tabular representation of actual Vs predicted values which helps us to find the accuracy of the model.
153. What are the advantages of SVM algorithms?
SVM algorithms have basically advantages in terms of complexity. First I would like to clear that both Logistic regression as well as SVM can form non linear decision surfaces and can be coupled with the kernel trick. If Logistic regression can be coupled with kernel then why use SVM?
● SVM is found to have better performance practically in most cases.
● SVM is computationally cheaper O(N^2*K) where K is no of support vectors (support vectors are those points that lie on the class margin) where as logistic regression is O(N^3)
● Classifier in SVM depends only on a subset of points. Since we need to maximize distance between closest points of two classes (aka margin) we need to care about only a subset of points unlike logistic regression.
154. Why does XGBoost perform better than SVM?
First reason is that XGBoos is an ensemble method that uses many trees to make a decision so it gains power by repeating itself.
SVM is a linear separator, when data is not linearly separable SVM needs a Kernel to project the data into a space where it can separate it, there lies its greatest strength and weakness, by being able to project data into a high dimensional space SVM can find a linear separation for almost any data but at the same time it needs to use a Kernel and we can argue that there’s not a perfect kernel for every dataset.
155. What is the difference between SVM Rank and SVR (Support Vector Regression)?
One is used for ranking and the other is used for regression.
There is a crucial difference between regression and ranking. In regression, the absolute value is crucial. A real number is predicted.
In ranking, the only thing of concern is the ordering of a set of examples. We only want to know which example has the highest rank, which one has the second-highest, and so on. From the data, we only know that example 1 should be ranked higher than example 2, which in turn should be ranked higher than example 3, and so on. We do not know by how much example 1 is ranked higher than example 2, or whether this difference is bigger than the difference between examples 2 and 3.
156. What is the difference between the normal soft margin SVM and SVM with a linear kernel?
Hard-margin
You have the basic SVM – hard margin. This assumes that data is very well behaved, and you can find a perfect classifier – which will have 0 error on train data.
Soft-margin
Data is usually not well behaved, so SVM hard margins may not have a solution at all. So we allow for a little bit of error on some points. So the training error will not be 0, but average error over all points is minimized.
Kernels
The above assume that the best classifier is a straight line. But what is it is not a straight line. (e.g. it is a circle, inside a circle is one class, outside is another class). If we are able to map the data into higher dimensions – the higher dimension may give us a straight line.
157. How is linear classifier relevant to SVM?
An svm is a type of linear classifier. If you don’t mess with kernels, it’s arguably the most simple type of linear classifier.
Linear classifiers (all?) learn linear fictions from your data that map your input to scores like so: scores=Wx + b. Where W is a matrix of learned weights, b is a learned bias vector that shifts your scores, and x is your input data. This type of function may look familiar to you if you remember y=mx + b from high school.
A typical svm loss function ( the function that tells you how good your calculated scores are in relation to the correct labels ) would be hinge loss. It takes the form: Loss=sum over all scores except the correct score of max(0, scores – scores(correct class) + 1).
158. What are the advantages of using a naive Bayes for classification?
Very simple, easy to implement and fast. If the NB conditional independence assumption holds, then it will converge quicker than discriminative models like logistic regression. Even if the NB assumption doesn’t hold, it works great in practice. Need less training data. Highly scalable. It scales linearly with the number of predictors and data points. Can be used for both binary and mult-iclass classification problems. Can make probabilistic predictions. Handles continuous and discrete data. Not sensitive to irrelevant features.
159. Are Gaussian Naive Bayes the same as binomial Naive Bayes?
Binomial Naive Bayes: It assumes that all our features are binary such that they take only two values. Means 0s can represent “word does not occur in the document” and 1s as “word occurs in the document”.
Gaussian Naive Bayes: Because of the assumption of the normal distribution, Gaussian Naive Bayes is used in cases when all our features are continuous. For example in Iris dataset features are sepal width, petal width, sepal length, petal length. So its features can have different values in the data set as width and length can vary. We can’t represent features in terms of their occurrences. This means data is continuous. Hence we use Gaussian Naive Bayes here.
160. What is the difference between the Naive Bayes Classifier and the Bayes classifier?
Naive Bayes assumes conditional independence, P(X|Y, Z)=P(X|Z)
P(X|Y,Z)=P(X|Z)
P(X|Y,Z)=P(X|Z), Whereas more general Bayes Nets (sometimes called Bayesian Belief Networks), will allow the user to specify which attributes are, in fact, conditionally independent.
For the Bayesian network as a classifier, the features are selected based on some scoring functions like Bayesian scoring function and minimal description length(the two are equivalent in theory to each other given that there is enough training data). The scoring functions mainly restrict the structure (connections and directions) and the parameters(likelihood) using the data. After the structure has been learned the class is only determined by the nodes in the Markov blanket(its parents, its children, and the parents of its children), and all variables given the Markov blanket are discarded.
161. In what real world applications is Naive Bayes classifier used?
Some of real world examples are as given below
To mark an email as spam, or not spam? Classify a news article about technology, politics, or sports? Check a piece of text expressing positive emotions, or negative emotions? Also used for face recognition software
162. Is naive Bayes supervised or unsupervised?
First, Naive Bayes is not one algorithm but a family of Algorithms that inherits the following attributes:
1.Discriminant Functions
2.Probabilistic Generative Models
3.Bayesian Theorem
4.Naive Assumptions of Independence and Equal Importance of feature vectors.
Moreover, it is a special type of Supervised Learning algorithm that could do simultaneous multi-class predictions (as depicted by standing topics in many news apps).
Since these are generative models, so based upon the assumptions of the random variable mapping of each feature vector these may even be classified as Gaussian Naive Bayes, Multinomial Naive Bayes, Bernoulli Naive Bayes, etc.
163. What do you understand by selection bias in Machine Learning?
Selection bias stands for the bias which was introduced by the selection of individuals, groups or data for doing analysis in a way that the proper randomization is not achieved. It ensures that the sample obtained is not representative of the population intended to be analyzed and sometimes it is referred to as the selection effect. This is the part of distortion of a statistical analysis which results from the method of collecting samples. If you don’t take the selection bias into the account then some conclusions of the study may not be accurate.
The types of selection bias includes:
Sampling bias: It is a systematic error due to a non-random sample of a population causing some members of the population to be less likely to be included than others resulting in a biased sample. Time interval: A trial may be terminated early at an extreme value (often for ethical reasons), but the extreme value is likely to be reached by the variable with the largest variance, even if all variables have a similar mean. Data: When specific subsets of data are chosen to support a conclusion or rejection of bad data on arbitrary grounds, instead of according to previously stated or generally agreed criteria. Attrition: Attrition bias is a kind of selection bias caused by attrition (loss of participants) discounting trial subjects/tests that did not run to completion.
164. What do you understand by Precision and Recall?
In pattern recognition, The information retrieval and classification in machine learning are part of precision. It is also called as positive predictive value which is the fraction of relevant instances among the retrieved instances.
Recall is also known as sensitivity and the fraction of the total amount of relevant instances which were actually retrieved.
Both precision and recall are therefore based on an understanding and measure of relevance.
165. What Are the Three Stages of Building a Model in Machine Learning?
To build a model in machine learning, you need to follow few steps:
Understand the business model Data acquisitions Data cleaning Exploratory data analysis Use machine learning algorithms to make a model Use unknown dataset to check the accuracy of the model
166. How Do You Design an Email Spam Filter in Machine Learning?
Understand the business model: Try to understand the related attributes for the spam mail Data acquisitions: Collect the spam mail to read the hidden pattern from them Data cleaning: Clean the unstructured or semi structured data Exploratory data analysis: Use statistical concepts to understand the data like spread, outlier, etc. Use machine learning algorithms to make a model: can use naive bayes or some other algorithms as well Use unknown dataset to check the accuracy of the model
167. What is the difference between Entropy and Information Gain?
The information gain is based on the decrease in entropy after a dataset is split on an attribute. Constructing a decision tree is all about finding the attribute that returns the highest information gain (i.e., the most homogeneous branches). Step 1: Calculate entropy of the target.
168. What are collinearity and multicollinearity?
Collinearity is a linear association between two predictors. Multicollinearity is a situation where two or more predictors are highly linearly related.
169. What is Kernel SVM?
SVM algorithms have basically advantages in terms of complexity. First I would like to clear that both Logistic regression as well as SVM can form non linear decision surfaces and can be coupled with the kernel trick. If Logistic regression can be coupled with kernel then why use SVM?
● SVM is found to have better performance practically in most cases.
● SVM is computationally cheaper O(N^2*K) where K is no of support vectors (support vectors are those points that lie on the class margin) where as logistic regression is O(N^3)
● Classifier in SVM depends only on a subset of points. Since we need to maximize distance between closest points of two classes (aka margin) we need to care about only a subset of points unlike logistic regression.
170. What is the process of carrying out a linear regression?
Linear Regression Analysis consists of more than just fitting a linear line through a cloud of data points. It consists of 3 stages–
(1) analyzing the correlation and directionality of the data,
(2) estimating the model, i.e., fitting the line,
(3) evaluating the validity and usefulness of the model.
“KickStart your Artificial Intelligence Journey with Great Learning which offers high-rated Artificial Intelligence courses with world-class training by industry leaders. Whether you’re interested in machine learning, data mining, or data analysis, Great Learning has a course for you!”
Also Read Top Common Interview Questions
Machine Learning Interview Questions FAQ’s
1. How do I start a career in machine learning?
There is no fixed or definitive guide through which you can start your machine learning career. The first step is to understand the basic principles of the subject and learn a few key concepts such as algorithms and data structures, coding capabilities, calculus, linear algebra, statistics. For better data analysis, You should have clear understanding of statistics for Machine Learning. The next step would be to take up an ML course or read the top books for self-learning. You can also work on projects to get a hands-on experience.
2. What is the best way to learn machine learning?
Any way that suits your style of learning can be considered as the best way to learn. Different people may enjoy different methods. Some of the common ways would be through taking up basics of machine learning course for free, watching YouTube videos, reading blogs with relevant topics, read books which can help you self-learn.
3. What degree do you need for machine learning?
Most hiring companies will look for a masters or doctoral degree in the relevant domain. The field of study includes computer science or mathematics. But having the necessary skills even without the degree can help you land a ML job too.
4. How do you break into machine learning?
The most common way to get into a machine learning career is to acquire the necessary skills. Learn programming languages such as C, C++, Python, and Java. Gain basic knowledge about various ML algorithms, mathematical knowledge about calculus and statistics. This will help you go a long way.
5. How difficult is machine learning?
Machine Learning is a vast concept that contains a lot different aspects. With the right guidance and with consistent hard-work, it may not be very difficult to learn. It definitely requires a lot of time and effort, but if you’re interested in the subject and are willing to learn, it won’t be too difficult.
6. What is machine learning for beginners?
Machine Learning for beginners will consist of the basic concepts such as types of Machine Learning (Supervised, Unsupervised, Reinforcement Learning). Each of these types of ML have different algorithms and libraries within them, such as, Classification and Regression. There are various classification algorithms and regression algorithms such as Linear Regression. This would be the first thing you will learn before moving ahead with other concepts.
7. What level of math is required for machine learning?
You will need to know statistical concepts, linear algebra, probability, Multivariate Calculus, Optimization. As you go into the more in-depth concepts of ML, you will need more knowledge regarding these topics.
8. Does machine learning require coding?
Programming is a part of Machine Learning. It is important to know programming languages such as Python.
Stay tuned to this page for more such information on interview questions and career assistance. You can check our other blogs about Machine Learning for more information.
You can also take up the PGP Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Course offered by Great Learning in collaboration with UT Austin. The course offers online learning with mentorship and provides career assistance as well. The curriculum has been designed by faculty from Great Lakes and The University of Texas at Austin-McCombs and helps you power ahead your career.
Further reading
Just like Machine Learning Interview Questions, here are a few other Interview Questions that might help you:
Python Interview Questions and Answers NLP Interview Questions and Answers Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions 100+ Data Science Interview Questions Hadoop Interview Questions SQL Interview Questions and Answers Rate this post
Sharing is caring!